Cooked chicken breast is a true staple in fitness diets. Many health-conscious individuals choose it as a go-to food. You know it as a lean protein source, which makes it critical for achieving various fitness objectives. Cooked chicken breast plays a huge role in your journey. We will explore the vital Cooked Chicken Breast Nutrition facts, fitness benefits, and practical uses of this amazing food. How can this simple chicken breast be such a powerful ally in your fitness journey? Discover its full potential. You will learn about its impressive protein and overall nutrition.
Cooked Chicken Breast Nutrition Profile

You want to understand what makes cooked chicken breast such a powerful food for your fitness goals. Let’s dive into the detailed nutrition facts of cooked chicken breast. This section breaks down its key components. You will see why it is a staple in healthy eating.
Key Macronutrients
When you examine the macronutrient breakdown of chicken breast, you find it is a powerhouse of protein. A 100-gram serving of cooked chicken breast gives you about 31 to 32 grams of protein. For example, some sources show 32.1 grams of protein, while others report approximately 31 grams. This makes it an excellent protein source. This high protein content is crucial for muscle growth and repair.
Cooked chicken breast is a complete protein. It contains all the essential amino acids your body needs. For instance, you get significant amounts of arginine, leucine, and lysine. These amino acids are vital for muscle repair and recovery. You also find histidine, methionine, and valine. Their content can even increase after cooking. This chicken breast is also very lean. It has only about 3-4 grams of fat per 100 grams. It has zero carbohydrates. This makes the chicken breast macros ideal for many diets. It is a truly low-fat protein option.
Vital Micronutrients
Beyond the main chicken breast macros, you also get vital micronutrients from cooked chicken breast. This chicken breast nutrition includes important vitamins. You receive a good amount of Niacin, about 14 milligrams. This covers 100% of the daily recommendation for adult women and 90% for men. You also get 1.3 mg of Vitamin B-6, meeting 100% of your daily needs. Other B vitamins like Thiamin, Riboflavin, and Vitamin B-12 are present. You also find small amounts of Vitamin D and B2.
Vitamin | Amount (micrograms/milligrams) |
|---|---|
Vitamin D | 0.1 – 0.2 micrograms |
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.114 – 0.227 milligrams |
Cooked chicken breast also provides essential minerals. You get phosphorus, around 220mg, and selenium, about 27.6mcg. These minerals are important for many body functions. Look at this chart to see more mineral details: You can see that chicken breast offers a good range of minerals like potassium, magnesium, and zinc. This comprehensive nutrition makes cooked chicken breast a valuable part of your diet.
Calorie Count
You want to know the calorie count for chicken breast. A 100-gram serving of cooked chicken breast typically contains around 157 to 165 calories. For example, Nutrition Facts Search Tool shows 157 calories for 100 grams of cooked chicken breast. FatSecret reports 165 calories for roasted, cooked chicken breast meat. MedicineNet also confirms 165 calories for a 100-gram cooked chicken breast. This calorie count applies to various preparations, including grilled, baked, boiled, and skinless chicken breast. This makes chicken breast calories a great choice for managing your calorie intake. It is a lean, high protein option that helps you stay full.
Fitness Benefits of Chicken Breast
Cooked chicken breast offers many advantages for your fitness journey. You can achieve your goals with this versatile food. It supports muscle development, helps manage your weight, boosts energy, and contributes to your overall well-being.
Muscle Growth and Repair
You know protein is essential for building and fixing muscles. Cooked chicken breast is an excellent protein source. It provides all the essential amino acids your body needs. These amino acids are the building blocks for muscle tissue. They help your muscles recover after exercise. For example, a 12-week study showed that older women who did resistance training and ate steamed chicken breast improved their muscle mass, strength, and quality. This means chicken breast protein helps your muscles adapt and recover after workouts.
Chicken breast is especially good if you want to keep your muscle mass or improve recovery. It has a high protein content by weight. Its lean nature and significant protein make it perfect for losing weight while keeping muscle. High protein foods support muscle building, muscle maintenance, and fat loss. Protein is vital for building lean muscle mass. Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat. This helps with weight loss. Meeting your daily protein needs is easy with chicken breast. This supports muscle gain and overall strength.
Weight Management Support
Chicken breast is a powerful tool for weight loss. It helps you feel full longer. This can reduce your overall calorie intake. Increasing your protein intake is a proven strategy for weight loss. It can boost your metabolism and reduce your appetite. It also helps decrease body fat while preserving muscle mass.
Chicken breast’s high protein content helps curb hunger. This leads to high satiety. You feel full and satisfied. This increased satiety can lead to a reduced calorie intake throughout the day. Eating lean protein snacks, like chicken breast, can stop late-night cravings. Pairing chicken breast with vegetables or a light whole-grain can make you feel even fuller. A 2011 study in Appetite found that chicken, beef, and pork created similar feelings of fullness. This shows chicken breast helps reduce hunger and aids in weight loss.
Energy and Performance Boost
You need energy for your workouts and daily activities. Chicken breast provides this energy. It contains important B vitamins. These vitamins help your body turn food into energy. Niacin (Vitamin B3) is vital for converting food into energy. Vitamin B6 supports brain function and energy metabolism. Pantothenic acid helps with hormone production and fat metabolism.
Chicken breast has B vitamins like thiamine, riboflavin, vitamin B6, niacin, pantothenic acid, and biotin. These are all involved in energy conversion during physical activity. Folate and vitamin B12 are also present. They are necessary for red blood cell production, protein synthesis, tissue repair, and maintenance. All these are crucial for athletic performance. Chicken breast is a low-calorie, nutrient-dense food. It has no carbohydrates. This makes it good for low-carb diets. These diets encourage your body to use fat for energy. This helps preserve muscle mass and gives you sustained energy during physical activity. The high protein in chicken breast also keeps you full. This helps you manage your weight. Maintaining a healthy weight supports sustained physical activity.
Overall Health Contributions
Eating chicken breast regularly offers many health benefits beyond fitness. It is a lean protein that supports heart health. The American Heart Association suggests lean poultry, like chicken breast, for a heart-healthy diet. A 2021 review showed that eating a lot of poultry does not negatively affect heart disease risk.
Chicken breast has low saturated fat. This is especially true compared to red or processed meats. This low fat content contributes to its heart health benefits. A 2022 review suggests that eating fresh lean white meat, like chicken breast, can positively affect cardiometabolic risk factors. Protein-rich meals, such as those with chicken, make you feel full. This leads to better weight management. A healthier weight improves risk factors for heart problems. These include high triglyceride levels and high blood pressure. Chicken, rich in protein, helps with weight loss. This reduces your risk of heart disease.
Preparing and Using Chicken Breast

You can easily incorporate chicken breast into your daily meals. Knowing how to prepare, store, and plan with it helps you maximize its benefits. This section guides you through practical tips for using this versatile protein.
Healthy Cooking Methods
You have many options for cooking chicken breast. Grilling, baking, poaching, and stir-frying are excellent choices. These methods require little added fat. For example, you can bake chicken breast with herbs and spices for a flavorful meal. Grilling gives you a smoky taste. Poaching keeps the chicken moist and tender, perfect for salads. When you stir-fry, you can combine chicken breast with plenty of vegetables for a balanced dish. Always cook chicken breast thoroughly.
Portion Control and Meal Planning
You can easily manage your protein intake with chicken breast. A typical serving size is about 3-4 ounces (around 100-120 grams). This provides a good amount of protein without excessive calories. You can cook a batch of chicken breast at the start of your week. Then, use it in various healthy diet recipes. This makes meal prep simple. You can add sliced chicken to salads, sandwiches, or pasta dishes. Planning your meals helps you stick to your fitness goals.
Food Safety and Storage
Food safety is crucial when handling chicken. Always wash your hands before and after touching raw chicken. Use separate cutting boards for raw meat. For safe consumption, all poultry, including chicken breasts, should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C). While 165°F (74°C) is the temperature at which foodborne bacteria are instantly eliminated for safety, you can often remove chicken breasts from heat at 157°F. This accounts for carryover cooking, where the internal temperature continues to rise after removal, ensuring both safety and optimal eating quality. Cooked chicken, whether fresh or uncured, can be safely stored in the refrigerator for 3 to 4 days.
Versatile Recipe Ideas
Chicken breast is incredibly versatile. You can create countless delicious and healthy recipes. Think about making chicken and vegetable skewers, a lean chicken curry, or a simple chicken stir-fry. For quick meals, prepare chicken breast salads or wraps. You can find many chicken breast recipes online. These recipes help you maintain a healthy diet while enjoying your food. Explore different spices and marinades to keep your meals exciting.
Comparing Chicken Breast with Other Proteins
You often wonder how chicken breast stacks up against other protein sources. Understanding these differences helps you make informed dietary choices. You can optimize your fitness goals.
Chicken Breast Versus Red Meat
You find chicken breast and red meat both offer excellent protein. However, they have key nutritional differences. Per 100 grams, chicken breast generally contains fewer calories and less fat than top sirloin steak. Both meats provide similar amounts of protein. Chicken breast has about 23 grams of protein, while sirloin offers 22 grams. Neither contains carbohydrates.
Nutrient | Beef (Sirloin, lean, grilled) (per 100g) | Chicken (Breast, skinless, grilled) (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
Calories (kcal) | 158 | 143 |
Protein (g) | 30.5 | 29.8 |
Total Fat (g) | 3.8 | 2.5 |
Saturated Fat (g) | 1.64 | 1.63 |
Iron (mg) | 2.2 | 0.4 |
Zinc (mg) | 7.8 | 0.68 |
Vitamin B12 (µg) | 1.4 | 0.5 |
Niacin (B3) (mg) | 1 | 6.9 |
You see beef provides more iron, zinc, and B12. Chicken breast offers more Niacin (B3). Chicken breast is a lean option. It has lower total fat. Dietary guidelines now focus more on limiting saturated fat than dietary cholesterol. Saturated fats impact your LDL cholesterol levels more. A 2019 study suggests that cholesterol levels may not differ significantly between chicken and red meat.
Chicken Breast Versus Fish
You can choose between chicken breast and fish for your protein needs. Both are excellent sources of high protein. A 3-ounce serving of skinless chicken breast gives you 26 grams of protein. Baked cod offers 22 grams. Both are complete proteins. They contain all essential amino acids.
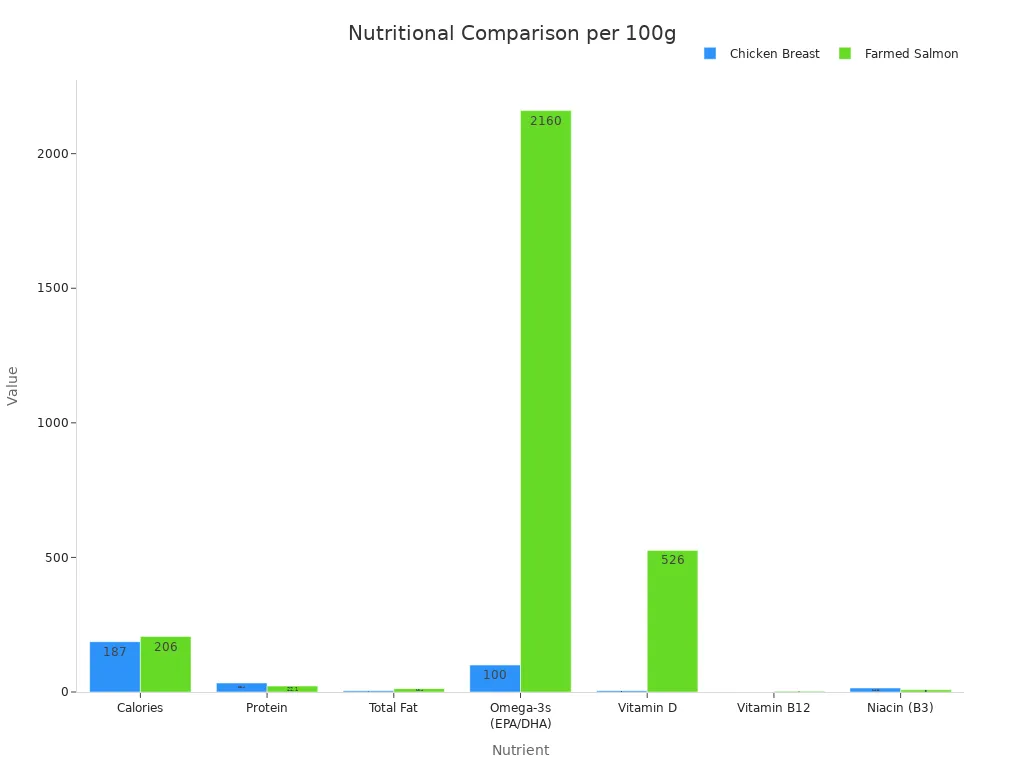
The main difference lies in fat content. Chicken breast is very lean. Fish, especially fatty fish like salmon, is rich in beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. These fats support heart and brain health. White fish, like cod, has less fat. For example, 3.5 ounces of farmed salmon contains 2,160 mg of Omega-3s. Chicken breast has less than 100 mg. Salmon also provides more Vitamin D and B12. Chicken breast offers more Niacin. You can include both in your diet for balanced nutrition.
Chicken Breast Versus Plant-Based Options
You might consider plant-based proteins. Chicken breast is a complete protein. It contains all essential amino acids. Many plant proteins, like lentils, are incomplete. They lack certain essential amino acids. You need to combine different plant proteins to get a complete profile. Tofu is a complete plant protein.
Animal proteins are highly digestible. Your body absorbs their amino acids efficiently. Plant proteins are often less digestible. This is due to fiber and other compounds. Chicken breast also offers more protein per calorie compared to most plant proteins. For example, three ounces of chicken has 24 grams of protein. A cup of chickpeas has 14.5 grams. Iron and zinc from meat are also more easily absorbed by your body than from most plant-based options.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
You will find chicken breast is a very accessible and cost-effective protein source. It is generally more affordable than beef. Some plant-based proteins, like soybeans or green peas, are cheaper per gram of protein. However, chicken breast offers a high protein density. This makes it a great value.
Protein Source | Cost per kg (100% equivalent protein) |
|---|---|
Beef | > $50 |
Whey Protein Concentrate | $17.13 |
Chicken | (Baseline for comparison) |
Chickpea Protein | At parity with chicken |
Premium Pea Protein | About the same as chicken |
Low-end Pea Protein | $7.02 (30% discount to chicken) |
Soy Protein Isolate | $2.68 |
Soybeans | $0.46 |
Green Peas | $0.32 |
Fluid Milk | $0.34 (low protein content) |
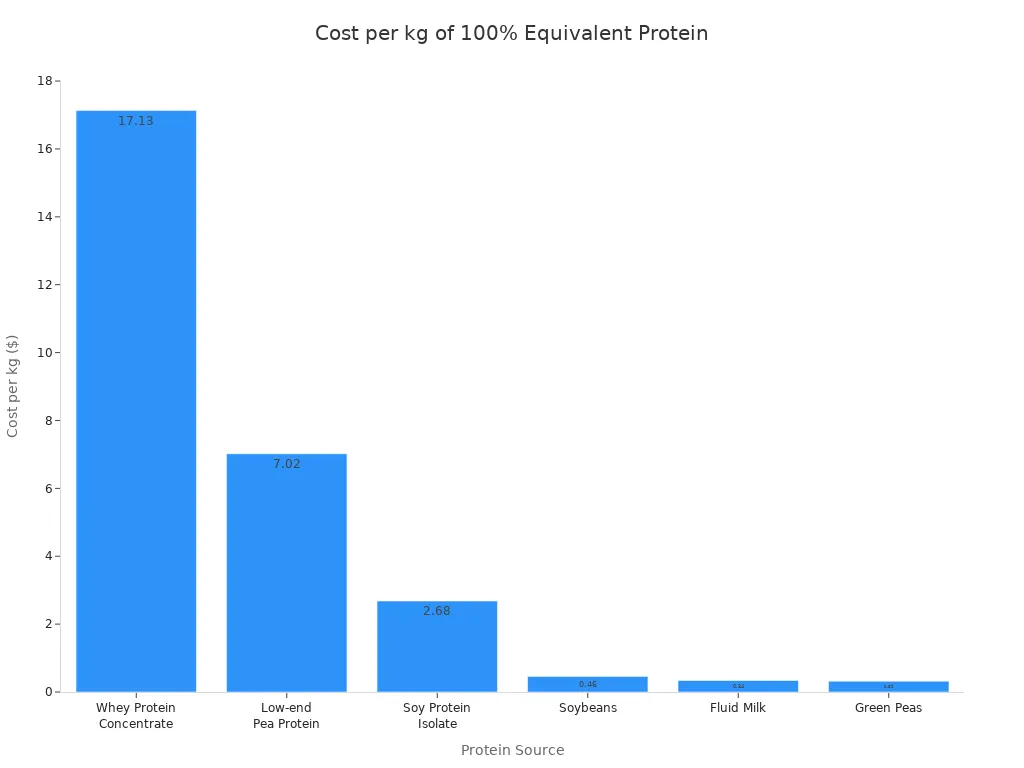
Soy protein isolate and low-end pea protein can be cheaper than chicken. However, chicken breast remains a popular choice. It offers a complete amino acid profile and high protein content.
Chicken Breast Myths and FAQs
You often hear different ideas about food. Let’s clear up some common misunderstandings about chicken breast. You can then make the best choices for your diet.
Debunking Nutritional Misconceptions
Some people think chicken breast is bland. They believe it lacks flavor or variety. This is not true. You can prepare chicken breast in many ways. It takes on flavors from spices and marinades very well. Others might think it lacks important vitamins. However, as you learned, chicken breast provides vital B vitamins and minerals. It offers excellent nutrition. It is a complete protein source. This means it gives you all the essential amino acids your body needs.
Addressing Cooking Concerns
You might worry about dry chicken breast. Many people overcook it. This makes it tough and dry. To avoid this, use a meat thermometer. Cook your chicken breast until it reaches an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C). You can even remove it at 157°F. It will continue cooking to a safe temperature. Brining or marinating also helps keep it moist. You can bake, grill, or poach it. These methods keep it tender.
Cooked chicken breast nutrition offers powerful benefits. It is crucial for muscle building and effective weight loss. Its high protein content supports fat loss and prevents muscle loss. These are key health benefits. You can easily integrate this versatile cooked chicken breast into your healthy diet. It helps you achieve your weight loss goals. This food aids in sustained weight loss. It prevents the loss of lean muscle. Make informed choices for a healthier, stronger you, ensuring no loss of progress in your weight loss journey.





