Is whole wheat bread truly healthy? Absolutely! Whole wheat bread is a nutritional powerhouse. It uses the entire whole grain kernel: the bran, germ, and endosperm. This makes it very different from refined white bread, which strips away much of the fiber and vital nutrients. You get more protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals with whole wheat bread. Understanding whole wheat bread nutrition helps you see its value.
This whole grain option offers significant benefits for your diet. Its rich fiber content aids digestion and helps stabilize blood sugar. Let’s explore its key nutrition facts and best uses.
Key Takeaways
Whole wheat bread uses the entire grain kernel. This gives you more fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals than white bread.
Fiber in whole wheat bread helps your digestion. It also supports a healthy heart and keeps your blood sugar steady.
Whole wheat bread can help you manage your weight. Its fiber makes you feel full longer, so you eat less.
Always check bread labels for “100% Whole Grain.” Make sure “Whole Wheat Flour” is the first ingredient to get real whole wheat benefits.
You can enjoy whole wheat bread in many meals. Pair it with healthy foods like avocado, nut butter, or lean protein for extra nutrition.
Whole Wheat vs. White Bread: Nutrition Facts

Understanding Whole Grain Components
You might wonder what makes whole wheat bread so different from its white counterpart. The answer lies in the grain itself. A true whole grain kernel has three main parts: the bran, the germ, and the endosperm. Whole wheat bread uses all three of these components. The bran is the outer layer. It is tough and protects the kernel. The germ is the embryo. It can sprout into a new plant. The endosperm is the largest part. It provides food for the germ.
White bread, however, uses only the endosperm. Manufacturers remove the bran and germ during processing. This process strips away many vital nutrients. When you choose whole wheat bread, you get the full benefits of the entire whole grain. This makes a big difference in its overall nutrition.
Key Nutritional Differences
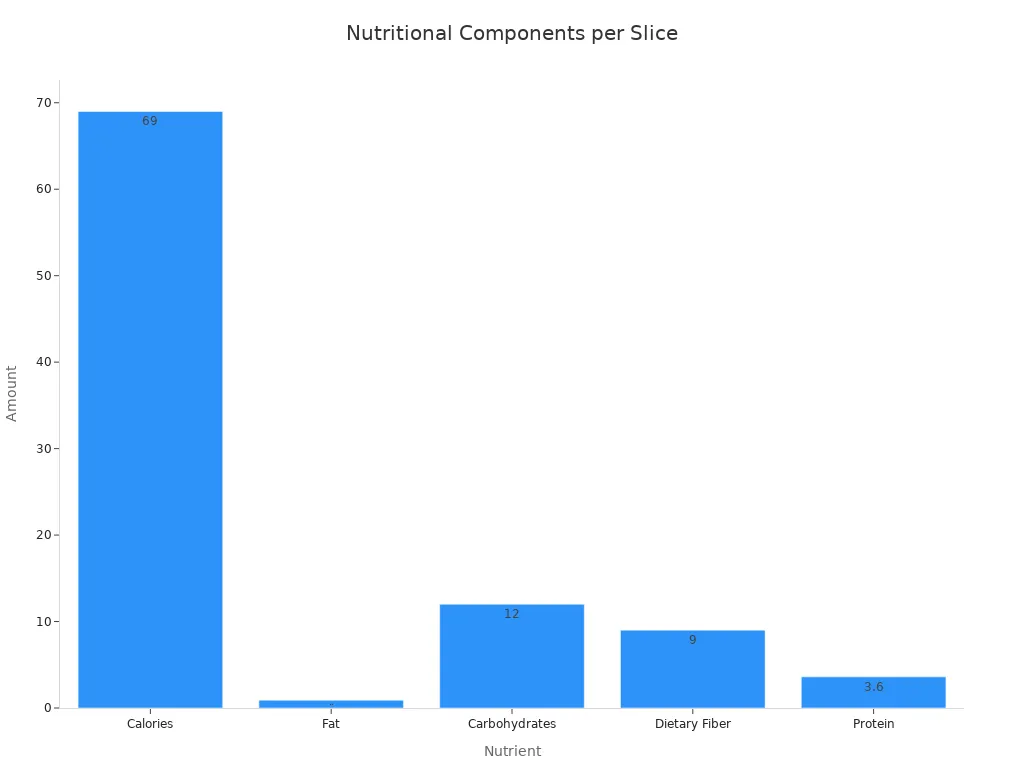
Let’s look at the specific nutrition facts. Whole wheat bread offers a superior nutritional profile compared to white bread. For example, a typical 43-gram slice of whole wheat bread provides about 80 calories. It also gives you around 3 grams of fiber. You get up to 5 grams of protein from that same slice. This means whole wheat bread contains 25 percent more protein than white bread. This extra protein helps you feel full and satisfied.
The bran in whole wheat bread is especially rich in dietary fiber. This fiber is crucial for your digestive system. The germ contains many important nutrients. These include vitamins, minerals, and lignans. Lignans are plant compounds with health benefits. White bread lacks these components. It offers fewer vitamins, minerals, and much less fiber. Therefore, when you compare the nutrition facts, whole wheat bread clearly stands out. It provides a more complete and beneficial nutrition package. You get a whole grain product that supports your health. This makes whole wheat bread nutrition a smart choice for your diet. It is higher in fiber and gives you more protein.
Fiber’s Role: Digestion & Health Benefits
Promoting Gut Health & Regularity
Fiber is very important for your digestive health. It helps your body in many ways. When you eat whole wheat bread, the fiber works to regulate your bowel movements. This helps prevent constipation and keeps things moving smoothly. Fiber also increases satiety, meaning you feel full longer after eating. This can help you manage your appetite.
The fiber in whole grain foods does amazing things in your gut. Your colon bacteria ferment this fiber. This process creates short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate. Butyrate is a main energy source for your colon cells. It helps them stay healthy and keeps your gut barrier strong. This fermentation also increases bacterial mass and fecal mass. This makes your stools larger and softer. It helps with easier bowel movements and reduces transit time. This is key for preventing or relieving constipation. SCFAs also lower the pH in your colon. This stops bad bacteria from growing and helps good bacteria, like bifidobacteria, thrive. Fiber holds water, and this, along with increased bacterial mass, directly contributes to heavier stools and better digestion.
You might wonder how much fiber you need. Adults in the US should aim for 25-35 grams of fiber each day. In the UK, the recommendation is 30 grams. Whole grain foods, like whole wheat bread, contribute to this goal. Even though all grain-based foods provide about 54.5% of total dietary fiber, only about 15.3% comes from whole grain foods. This shows you need to actively choose whole grain options to get enough fiber.
Supporting Heart Health
Beyond digestion, fiber offers significant health benefits for your heart. Eating more dietary fiber is linked to a lower risk of heart problems. Scientific evidence shows that higher fiber intake can reduce deaths from cardiovascular disease. It also lowers the chances of getting cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease, and stroke. This is a strong finding from many studies.
Fiber helps your heart by reducing total cholesterol and “bad” low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in your blood. This is a key mechanism for protecting your heart. The nutrients and phytochemicals in whole grain foods also play a role. These include Vitamin E, selenium, B vitamins, iron, magnesium, zinc, and potassium. They work together to support your overall heart health.
Aiding Blood Sugar Regulation
Whole wheat bread and its fiber content are excellent for blood sugar control. The fiber, nutrients, and phytochemicals in whole grains can improve how your body uses insulin. They also help with glucose metabolism. This means your body processes sugar more effectively. They slow down how fast your body absorbs food. This leads to more stable blood sugar levels.
Many compounds in whole grains contribute to better blood sugar control. For example, cyanidin can reduce blood glucose levels. Beta-cryptoxanthin is an antioxidant linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Lutein may help prevent cataracts in people with diabetes. Zeaxanthin could stop retinopathy from developing. Barley beta-glucan effectively reduces glucose and insulin responses. Quercetin can lower blood glucose and improve insulin levels. Ferulic acid helps reduce oxidative stress. Saponin can lower blood glucose. Vitamin E improves insulin sensitivity. Phytic acid can lower blood glucose after meals by slowing starch digestion. Gamma-oryzanol increases insulin sensitivity.
Studies consistently show that eating whole grains is linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Diets with whole grains significantly decrease blood glucose and insulin levels compared to high glycemic index diets. This is true for both healthy people and those with diabetes. Whole grain flour also leads to lower circulating glucose and insulin levels compared to refined grain flour. Research suggests that eating whole grains can make your body more sensitive to insulin. This is crucial for effective blood sugar control.
A study by Liu et al. (2018) showed that eating black-grained wheat improved blood sugar control and inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes. However, a review of studies found that while whole grain consumption reduced fasting glucose in healthy people, it did not significantly affect blood sugar control in people with hyperglycemia, including those with diabetes. This means whole wheat bread is a great choice for general blood sugar control and prevention, but its direct impact on existing diabetes management might vary for specific glucose measures. Still, it remains a valuable part of a diet for overall blood sugar control.
Whole Wheat for Weight Management
Fiber’s Impact on Satiety
Whole wheat bread can be a great ally in your weight management journey. Its high fiber content plays a big role. Fiber helps you feel full longer. This feeling of fullness, or satiety, means you eat less overall. When you choose whole grain foods, you often consume a greater volume of food for the same amount of available carbohydrates compared to refined grains. This increased volume helps you feel more satisfied.
Studies show that eating whole grains can reduce hunger and desire to eat, even many hours later. This long-term effect on appetite might come from slower digestion or the fermentation of fibers in your colon. For example, a whole grain evening meal can slow down how fast your stomach empties at breakfast. This leads to greater satiety after breakfast. Fermentation also produces short-chain fatty acids. These stimulate hormones that increase feelings of fullness and reduce how much energy you take in.
Calorie Intake & Nutrient Density
Whole wheat bread helps you manage your calorie intake. It has a lower energy density than refined grains. This means you get more food volume for fewer calories. Substituting whole grain foods for refined ones often increases your dietary fiber intake. This also reduces energy density. Both factors lead to lower daily calorie consumption and less weight gain over time.
Whole wheat bread also has a lower glycemic index. This means it causes a slower, more gradual rise in your blood sugar. This steady increase prevents sharp insulin spikes. It helps you maintain energy levels longer, stopping you from overeating. A 2012 study found that people who ate whole grains instead of refined grains lost more body weight and fat, especially around their abdomen. This was due to the high fiber, which made them feel fuller and reduced their overall calorie intake.
Whole grains also contain more protein than refined grains. Choosing bread with higher protein content is good for weight loss. Protein increases satiety, helping you feel fuller for longer. Protein also requires more energy to digest. It helps preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss, which is important for a healthy metabolism. This makes whole wheat bread a smart choice for your nutrition goals.
Identifying Real Whole Wheat Bread

Decoding Food Labels
You want to choose the best whole wheat bread. First, look for the “100% Whole Grain” stamp on the package. This stamp tells you the product is truly whole grain. It means the bread contains all the good parts of the grain. Next, check the ingredient list carefully. Make sure “Whole Wheat Flour” is the very first ingredient. This is a key sign. It indicates the product contains the entire grain kernel. This includes the bran, the germ, and the endosperm. These components are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and other health-promoting compounds. Refined grains lack these important nutrients. This simple check helps you pick a truly nutritious whole wheat bread. You ensure you get the full benefits of the whole grain.
Avoiding Misleading Terms
Some labels can confuse you. The term ‘whole-wheat’ on bread labels can be tricky. Manufacturers can process the grain. They separate its parts. This can transform a potentially nutritious grain. It can become something like sugary white bread. This happens even with the ‘whole-wheat’ claim. Many people find it hard to identify truly healthy products. They often understand these products as just less processed. They do not always know whole grain means containing all components of the grain. This difficulty makes it harder to choose well.
Also, rules for ‘whole grain’ claims are not always strict in some places. Many consumers do not actively look for the term ‘whole grains’ on packages. This is true even though these claims are common on breakfast cereals and breads. So, always check the ingredient list for your whole wheat bread. Do not just trust the front label. Make an informed choice for your health.
Best Uses & Pairings for Whole Wheat
Versatile Meal Applications
You can easily make whole wheat bread a part of your daily meals. It works well at any time of day. For breakfast, you can toast it. Add some avocado or a poached egg. This gives you a great start to your morning. At lunchtime, use it for sandwiches. Fill it with lean protein and lots of vegetables. This makes a satisfying and healthy meal. You can also serve it alongside a hearty vegetable soup for dinner. Whole wheat bread also makes a good snack. Top it with cottage cheese or a nut butter. This gives you energy between meals.
Complementary Food Pairings
Pairing whole wheat bread with other foods boosts its benefits. You enhance both flavor and nutrition. Consider these excellent combinations:
Avocado: It provides healthy fats and fiber.
Nut Butters (like peanut butter or almond butter): These offer protein and healthy fats for an energy boost.
Tomato and Cucumber: They supply vitamins and minerals. This makes a refreshing option.
Hummus: This is high in protein. It makes a filling and satisfying topping.
Poached Egg (with avocado toast): This balances healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
Banana (with nut butter toast): It combines carbohydrates with healthy fats for a satisfying meal.
Grilled Vegetables (with hummus sandwich): This offers a plant-based, fiber-rich choice.
Turkey: It provides a protein boost.
Spinach: It adds greens and nutrients to a high-protein lunch.
Cottage Cheese: This is a protein-rich snack.
Hearty Vegetable Soup: It creates a comforting and balanced meal.
Tomatoes, Basil, and Olive Oil (for bruschetta): This offers a healthy topping with fresh ingredients.
These pairings help you get more nutrients. They also make your meals more enjoyable. You can explore many delicious ways to include whole wheat bread in your diet.
Whole wheat bread nutrition offers many benefits. Its significant fiber content supports digestion and heart health. You also get B vitamins, magnesium, and antioxidants. These are crucial health benefits. Remember, refining grains removes these vital components. Always choose genuine whole wheat products. Make informed choices for your long-term well-being.
FAQ
Is whole wheat bread always better than white bread?
Always check labels. Look for “100% Whole Grain” and “Whole Wheat Flour” as the first ingredient. Some “whole wheat” breads contain added sugars or refined flours. You want the real deal for full benefits. You get more fiber and nutrients from truly whole grain options.
Can whole wheat bread help you lose weight?
Yes, it can. Its high fiber content helps you feel full longer. This reduces overall calorie intake. You eat less because you feel satisfied. This supports your weight management goals. You will find it a helpful part of your diet.
How much whole wheat bread should you eat daily?
You can include 2-3 servings of whole grains daily. One slice of whole wheat bread counts as a serving. Balance it with other whole grains like oats or brown rice. You should fit it into your balanced diet. You will get enough fiber this way.
Does whole wheat bread affect blood sugar?
Whole wheat bread has fiber. This fiber slows sugar absorption. It helps keep your blood sugar levels stable. This is beneficial for managing blood sugar. It can be a good choice if you are concerned about blood sugar or diabetes.





